Showing posts with label is. Show all posts
Showing posts with label is. Show all posts
Monday, March 27, 2017
What is Kali Linux
What is Kali Linux
Kali Linux is an advanced Penetration Testing and Security Auditing Linux Distribution, based on Debian development standards. Kali Linux- a complete re-built of Backtrack Linux, was developed by Offensive Security. Kali Linux is completely open source and come free of cost. It offers more than 300 penetration testing tools with timely security updates, support for the ARM architecture, a choice of four popular desktop environments and seamless upgrades to newer versions. Kali Linux is distributed in 32-bit and 64-bit images for use on hosts based on the x86 processor architecture, as well as an image for the ARM architecture for use on the Raspberry Pi computer, rk3306 mk/ss808, ODROID U2/X2 and on Samsungs ARM Chromebook.
Earlier release of Kali Linux:
Kali 1.0.2 – 27th March, 2013 – Minor Bugfix Release and update roll-up.
Kali 1.0.1 – 14th March, 2013 – Minor Bugfix Release.
Kali 1.0 – 13th March, 2013 – Initial release.
Available link for download
Friday, March 24, 2017
What is Slave Select SS in SPI
What is Slave Select SS in SPI
There’s one last line you should be aware of, called SS for Slave Select. This tells the slave that it should wake up and receive / send data and is also used when multiple slaves are present to select the one you’d like to talk to.
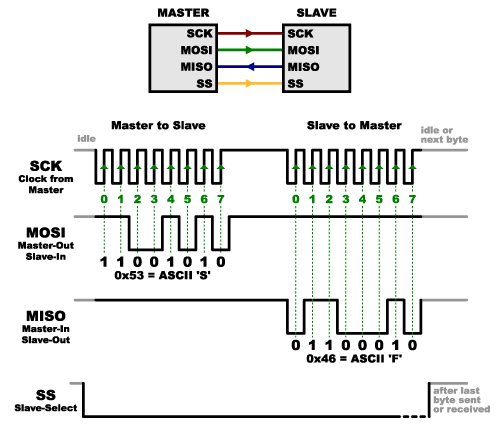
The SS line is normally held high, which disconnects the slave from the SPI bus. (This type of logic is known as “active low,” and you’ll often see used it for enable and reset lines.) Just before data is sent to the slave, the line is brought low, which activates the slave. When you’re done using the slave, the line is made high again. In a shift register, this corresponds to the “latch” input, which transfers the received data to the output lines.
Multiple slaves
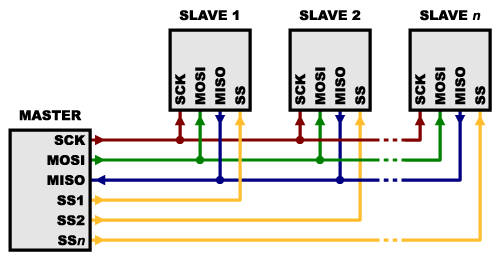
There are two ways of connecting multiple slaves to an SPI bus:
- In general, each slave will need a separate SS line. To talk to a particular slave, you’ll make that slave’s SS line low and keep the rest of them high (you don’t want two slaves activated at the same time, or they may both try to talk on the same MISO line resulting in garbled data). Lots of slaves will require lots of SS lines; if you’re running low on outputs, there are binary decoder chips that can multiply your SS outputs.
- On the other hand, some parts prefer to be daisy-chained together, with the MISO (output) of one going to the MOSI (input) of the next. In this case, a single SS line goes to all the slaves. Once all the data is sent, the SS line is raised, which causes all the chips to be activated simultaneously. This is often used for daisy-chained shift registers and addressable LED drivers.
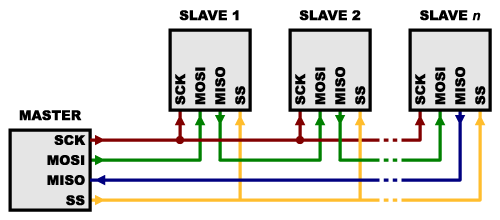
Note that, for this layout, data overflows from one slave to the next, so to send data to any one slave, you’ll need to transmit enough data to reach all of them. Also, keep in mind that the first piece of data you transmit will end up in thelast slave.
This type of layout is typically used in output-only situations, such as driving LEDs where you don’t need to receive any data back. In these cases you can leave the master’s MISO line disconnected. However, if data does need to be returned to the master, you can do this by closing the daisy-chain loop (blue wire in the above diagram). Note that if you do this, the return data from slave 1 will need to pass through all the slaves before getting back to the master, so be sure to send enough receive commands to get the data you need.
Source :https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/serial-peripheral-interface-spi/slave-select-ss
Available link for download
Monday, March 20, 2017
What Is Buoyant Force
What Is Buoyant Force
What Is Buoyant Force?
Buoyant force is an upward force that fluids exerts on any object that is placed in them. The ability of fluids to exert this force is called buoyancy . What explains buoyant force? A fluid exerts pressure in all directions, but the pressure is greater at greater depth. Therefore, the fluid below an object, where the fluid is deeper, exerts greater pressure on the object than the fluid above it. You can see in theFigure below how this works. Buoyant force explains why the girl pictured above can float in water. ?

Q : You’ve probably noticed that some things don’t float in water. For example, if you drop a stone in water, it will sink to the bottom rather than floating. If buoyant force applies to all objects in fluids, why do some objects sink instead of float?
A : The answer has to do with their weight.
Weight and Buoyant Force
Weight is a measure of the force of gravity pulling down on an object, whereas buoyant force pushes up on an object. Which force is greater determines whether an object sinks or floats. Look at the Figure below . On the left, the object’s weight is less than the buoyant force acting on it, so the object floats. On the right, the object’s weight is greater than the buoyant force acting on it, so the object sinks.

Because of buoyant force, objects seem lighter in water. You may have noticed this when you went swimming and could easily pick up a friend or sibling under the water. Some of the person’s weight was countered by the buoyant force of the water.
Density and Buoyant Force
Density, or the amount of mass in a given volume, is also related to the ability of an object to float. That’s because density affects weight. A given volume of a denser substance is heavier than the same volume of a less dense substance. For example, ice is less dense than liquid water. This explains why the giant ice berg in the Figure below is floating in the ocean. You can see other examples of density and buoyant force at this URL:
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VDSYXmvjg6M

Q : Can you think of more examples of substances that float in a fluid because they are low in density?
A : Oil is less dense than water, so oil from a spill floats on ocean water. Helium is less dense than air, so balloons filled with helium float in air.
Summary
- Buoyant force is an upward force that fluids exert on any object that is placed in them. Buoyant force occurs because the fluid below an object exerts greater pressure on the object than the fluid above it.
- If an object’s weight is less than the buoyant force acting on it, then the object floats. If an object’s weight is greater than the buoyant force acting on it, then the object sinks.
- A given volume of a denser substance is heavier than the same volume of a less dense substance. Therefore, density of an object also affects whether it sinks or floats.
Available link for download
Wednesday, March 15, 2017
What is Quiescent Current
What is Quiescent Current
The term given to describe the amount of current consumed by a circuit when it is not performing any work (sometimes referred to as standby current). This is a particularly important concept in designing battery-operated systems such as wireless beltpack transmitters. Battery life is determined by the total current drain composed of quiescent current and load current. Usually battery-operated devices are in standby mode more than in operation mode so the quiescent current consumption is the more dominant consideration. Quiescent current consumption should be as low as possible in order to prolong the battery’s life.
Class A amplifiers have the general property that the output device(s) always carry a significant current level, and hence have a large quiescent current. The quiescent current is defined as the current level in the amplifier when it is producing an output of zero. Class A amplifiers vary the large quiescent current in order to generate a varying current in the load, hence they are always inefficient in power terms.
Source: http://www.sweetwater.com/insync/class/
Available link for download
Saturday, February 25, 2017
Basic Electricity What is an amp
Basic Electricity What is an amp
Basic Electricity - What is an amp.
Watt Is An Amp?
Frequently Asked Question:
What is a watt? What is an amp? And why is it important for me to know how many watts or amps my equipments draws? This is a very good and much asked question. Its important to know how much electricity your equipment consumes, because all sources of power are finite. Whether youre connected to a battery, a standard AC wall outlet, or the power pole outside your theater, theres a limit to the quantity of power available (albeit a pretty BIG limit, when it comes to the poles power line :-) This answers the last
part of the question, because knowing the wattage or amperage (along with the voltage) allows you to determine the type of power source required to operate your equipment. Now the first parts . . . An amp is a unit of electrical current. The quantity tells you how much electricity is being drawn through the power cable. A product that draws 10 amps sucks twice as much electricity as a product that draws 5 amps. (Thats why it needs thicker wires.) A watt is a unit of electrical power. The quantity tells you how quickly electricity is being consumed through the power cable. "Consumption" differs from "draw" in that its relative to voltage, while draw is not. Two products may both draw 5A (5 amps), but if one is 12V and the other 6V, the 12V product will consume twice as much electricity as the 6V product. The 12V product will consume twice as many watts as the 6V product, even though they both draw amps at the same rate.* P=IV Power = Current x Voltage Watts = Amps x Volts All of these equations say the same thing. You multiply amps by volts to determine watts. Or you divide volts into watts to determine amps. Most equipment will specify the voltage required, and either the current draw (amps) or power consumption (watts); once you know two of the figures, you can use the above equation to calculate the third. An example is in order. Most electrical products draw 120 VAC. Most electrical circuit breakers are rated at 20A. 20x120=2,400; therefore, you can plug 2,400W of equipment into most AC wall outlets and know that the breaker will not kick.** Well thats pretty much it for watts and amps. * Purists may flame me for using the term "consumption" in association with "Watts", but I believe I made it clear that I was talking about the "rate" of consumption, not the actual consumption itself. Power "consumption" is measured in Watt-Seconds, or Joules. (But unless you plan to dispute your electric bill with the utility company, its really not necessary for you to know this. :) ** An individual standard wall outlet is usually rated at 15A. There are usually a number of these outlets on one 20A breaker. You can draw a total of 2,400W by using two or more of these outlets. You cant actually plug 2,400W into one 15A outlet, as the article may have implied.
Available link for download
Thursday, February 23, 2017
How to fix stop c0000221 bad image checksum the image user32 dll is possible corrupt the header checksum does not match the computed checksum
How to fix stop c0000221 bad image checksum the image user32 dll is possible corrupt the header checksum does not match the computed checksum
Stop: c0000221 {bad image checksum}
the image user32.dll is possible corrupt. the header checksum does not match the computed checksum.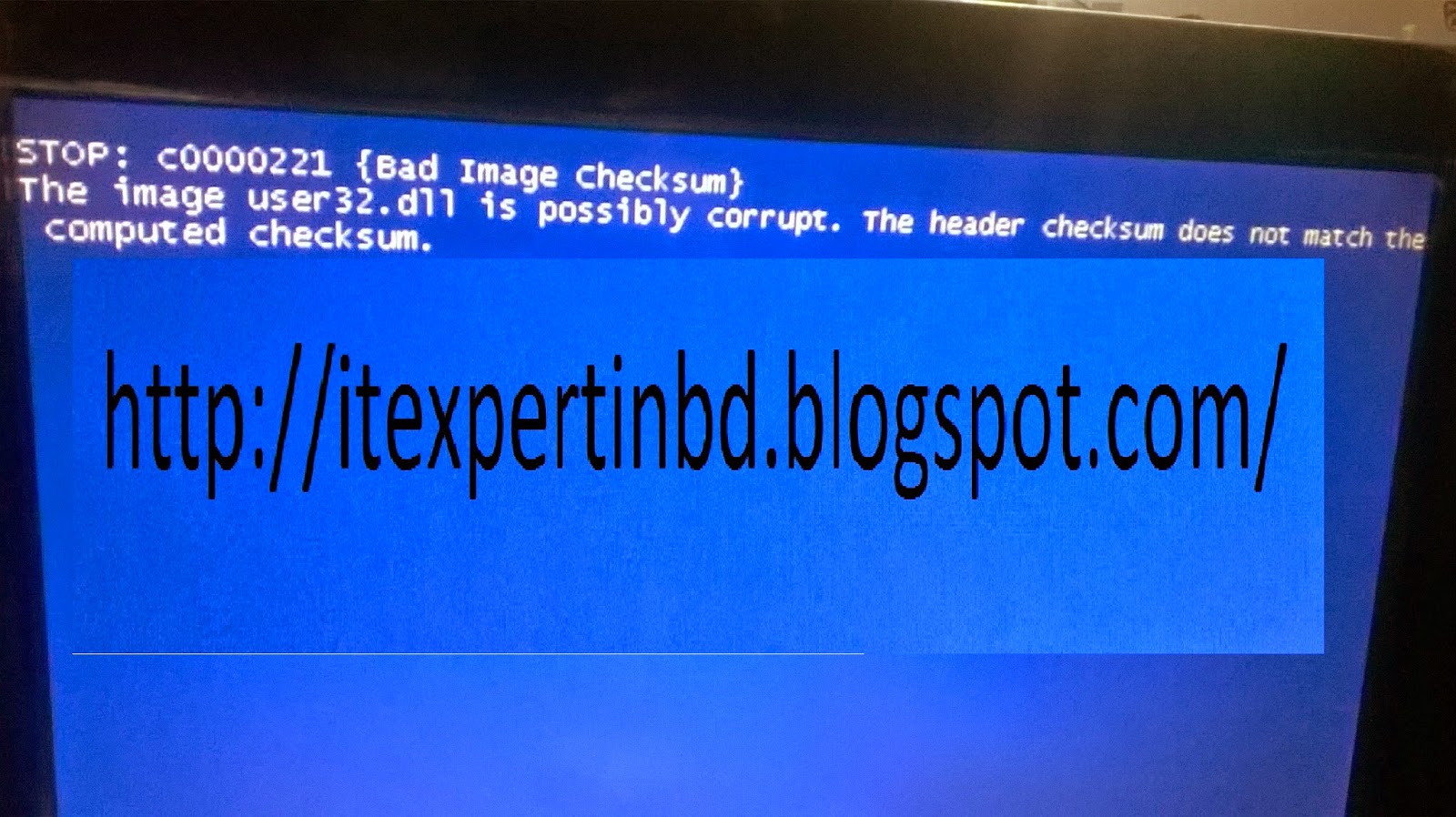 |
| Add caption |
Method 1: Extract a New Copy of the User32.dll File from the Windows XP CD
Method 2: Remove or Replace the Faulty RAM
Method 3: Replace hard disk or fix hdd bad sectors.
"how to fix Error! STOP:C0000221", "how to solve Error! STOP:C0000221", "how to fix stop: c0000221 {bad image checksum}", "how to solve stop: c0000221 {bad image checksum}"
Available link for download
Sunday, February 19, 2017
What is a constant power load Constant current load and Constant resistance load
What is a constant power load Constant current load and Constant resistance load
Constant resistance load:
In a constant resistance load the current will go down in proportion to the voltage drop as the resistance is fixed and the load must follow ohms law. Heaters approximate this type of load.
Constant current load:
In a constant current load the load will dynamically adjust its resistance as the voltage drops to keep the current constant. Thus as the battery voltage drops so will the equivalent resistance of the load. Older linear regulators using a pass transistor to deliver constant voltage to a fixed load powering electronics are this kind of load.
Constant power load:
In a constant power load, the dynamic resistance is adjusted to increase the current inversely to the load voltage. as the voltage rises or falls, then the product of voltage and current in the load is power which is constant. This is done to keep the power dissipated in the load constant as the voltage drops. Electronics devices with SMPS approximate this type of load as they generally employ regulators to generate a constant voltage and when then runs the electronics.
Real loads usually approximate one of the three types of load. Electrical engineers have as one of their tools electronics loads which can be programmed to emulate the load types above.
Source : Quora
In a constant resistance load the current will go down in proportion to the voltage drop as the resistance is fixed and the load must follow ohms law. Heaters approximate this type of load.
Constant current load:
In a constant current load the load will dynamically adjust its resistance as the voltage drops to keep the current constant. Thus as the battery voltage drops so will the equivalent resistance of the load. Older linear regulators using a pass transistor to deliver constant voltage to a fixed load powering electronics are this kind of load.
Constant power load:
In a constant power load, the dynamic resistance is adjusted to increase the current inversely to the load voltage. as the voltage rises or falls, then the product of voltage and current in the load is power which is constant. This is done to keep the power dissipated in the load constant as the voltage drops. Electronics devices with SMPS approximate this type of load as they generally employ regulators to generate a constant voltage and when then runs the electronics.
Real loads usually approximate one of the three types of load. Electrical engineers have as one of their tools electronics loads which can be programmed to emulate the load types above.
Source : Quora
Available link for download
Saturday, February 18, 2017
Is You Antivirus Working Perfect
Is You Antivirus Working Perfect
Is You Antivirus Working Perfect ?

More Tricks
- Keyboard Dancing Led Light Trick
- Learn To Make Dangerous Virus In A Minute
- How To Open Number Of Sites With A Single Click ?
- How to Lock a Folder in Windows 7/8/8.1
This trick will let you detect whether your antivirus software is working or is just a waste. We will create a file which every antivirus sofware will detect as virus but dont worry it is harmless and will not harm your computer.
- First open Notepad and copy below code into it.
X5O!P%@AP[4PZX54(P^)7CC)7}$EICAR-STANDARD-ANTIVIRUS-TEST-FILE!$H+H*
- Save the file as virus.exe

Note:-As always, if you would like to leave a sensible comment, then please do so in the comments section below.
Available link for download
Friday, February 17, 2017
What is Motherboard
What is Motherboard
 |
| What is Motherboard? |
1.What is Motherboard?
The motherboard serves to connect all of the parts of a computer together. The CPU, memory, hard drives, optical drives, video
card, sound card etc. connect to the motherboard directly or via cables.Available link for download
Labels:
is,
motherboard,
what
Thursday, February 16, 2017
STOP c0000135 the program cant start because hs is missing Try reinstalling the program Blue Screen error
STOP c0000135 the program cant start because hs is missing Try reinstalling the program Blue Screen error
This BSOD error occurs due to corrupted registry files and it is caused by some hijackers, viruses, malwares etc. More recently my PC crashes frequently and restarts every time. Then I decide to boot my PC with the function "Disable Automatic Restart on system failure" during start up and it stops at this blue screen of death.
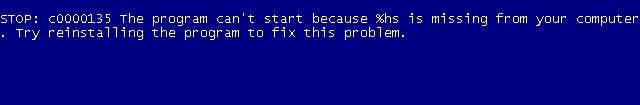
After spending several time in fixing this issue with offline registry editors, again PC crashes with another BSOD error soon after fixing the previous one. It was a fatal system error report and now it was really a bad time for me.
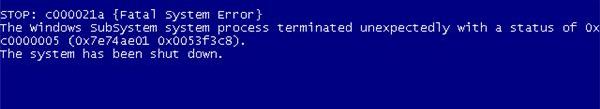
STOP: c000021a {Fatal System Error} - This was the error faced by me. Very soon, (by luck) Ive have found another solution which saves my whole work and no longer the bad time continues. I think this was the entire solution for both the BSOD errors mentioned above.
Solution: (for Vista/7 Users)
[Last Updated on July 8, 2012]
[Last Updated on July 8, 2012]
By luck, if you found to have RegBack folder in C:WindowsSystem32Config then this was perfect fix. Simply copy all those files which is inside this folder and paste it outside the folder and replace all with same name. Hurray, you have won!
- Also check if there was any *.LOG1, *.LOG2 files in config folder and dont forgot to delete these since they are the virus programs which infects the registry files and make us unable to logon by crashing.
- These virus LOG files can be easily identified since it does not have any file type. In actual, all log files have file type as text document. To verify you can see their file properties.
If you are clueless on how to access this folder without encountering this BSOD error, I suggest some methods here.
Method1
Launching Recovery Console by pressing F8 key before Start-up screen appears to bring up eight functions menu > select Repair your computer option > Select your language for keyboard layout > Type the password for user account > Select command prompt from System Recovery options.
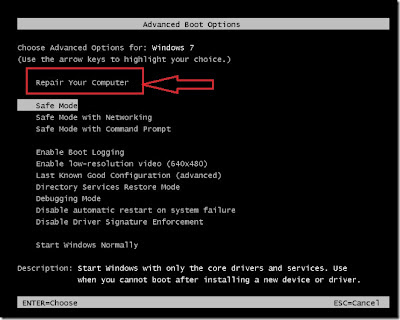
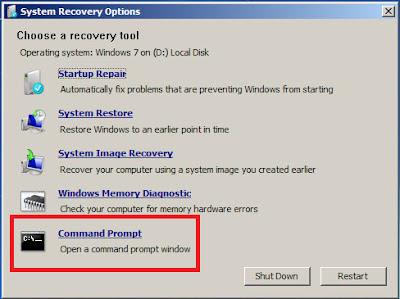
Method2
Using windows setup dvd (or) recovery disc. Boot the PC from dvd drive > press any key to boot from cd (if it asks) > select your language > click Repair your computer below the Install button.
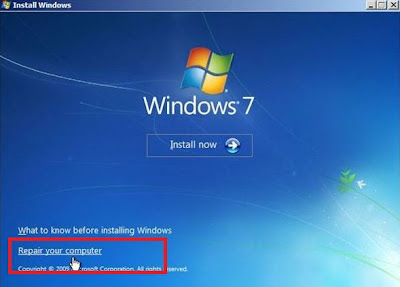
click "Use Recovery tools that can help fix problems starting windows" radio button and select the operating system and click Next > and then select command prompt from System Recovery options.
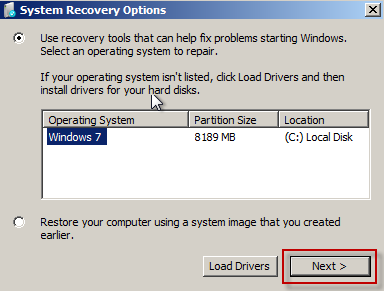
Method3
If you have installed two OS on same PC, then it is easy to access this folder by logging into the other operating system whether it is XP/Vista/7/RedHat linux/Ubuntu/Fedora.
Method3
Using other third-party bootable dvds like Ophcrack LiveCD, Ubuntu LiveCD, Hirens BootCD.
Method4
Connecting your internal hard disk to another PC or laptop via IDE/SATA to USB adapter. For more to know read my post on How to use internal Hard disk as an external USB device.
Using Command prompt
1. Type cd<space>C:WindowsSystem32Config and hit Enter key.
2. Now type dir and hit Enter key.
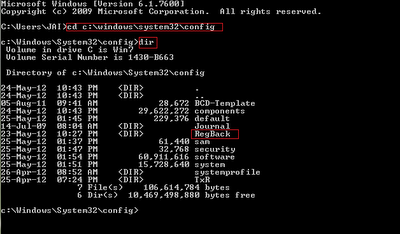
3. Type the following commands as follows and press Enter key after each.
- cd RegBack
- copy *.* c:WindowsSystem32config
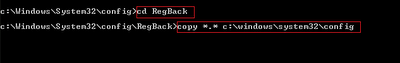
4. If it ask for overwrite any existing files (y/n) > type Y and press Enter.
5. If all files were successfully copied message is displayed, type exit to leave the command prompt and restart Windows.
Finally, if you couldnt find RegBack folder; thinking that I was wasting your time.
GO AHEAD! - FORMAT YOUR PC! - INSTALL NEW OS!
But this is not the end for XP users. Read this Microsoft article on How to recover from a corrupted registry that prevents Windows XP from starting.
Overall, the above choice is my best advice rather than editing registry files directly.
Note: If you are still interested in editing those registry files, read my post on STOP: c0000135 error - Solved using Registry Editor.
But this is not the end for XP users. Read this Microsoft article on How to recover from a corrupted registry that prevents Windows XP from starting.
Overall, the above choice is my best advice rather than editing registry files directly.
Note: If you are still interested in editing those registry files, read my post on STOP: c0000135 error - Solved using Registry Editor.
Available link for download
Sunday, January 29, 2017
What is 555 Timer How it Works
What is 555 Timer How it Works
555 Timer
Timers
Timers are those circuits, which provide periodic signals to a digital system which change the state of that system. In other words, those circuits, which work on the base of multivibrator changes or a device, which can be used as multivibrator is called Timer. (We will discuss Multivibrator in detail in next coming posts)
555 Timer
555 Timer is a digital monolithic integrated circuit which may be used as a clock generator. In other words, 555 Timer is a circuit which may be connected as a stable or monostable multivibrator.
555 Timer is a versatile and most usable device in the electronics circuits and designs which work for both stable and monostable states. It may provide time delay from microseconds up to many hours.
Below is the pin diagram of DIP (Dual inline Package) 555 timer with 8 pins.
555 timer is a very cheap IC which works for wide range of potential difference (typically, from 4.5 to 15V DC) and the different provided input voltages do not affect the timer output.
555 Timer is a linear device and it can be directly connected to the CMOS or TTL (Transistor – Transistor Logic) digital circuits due to its compatibility but, interfacing is must to use 555 timer with other digital circuits.
555 Timer Construction
There are lots of manufacturers who manufacture 555 timer which included the number 555 e.g. NE555, CA555, SE555, MC14 555 etc. typically, two 555 timers sandwiched inside a single chip which is called 556. Nowadays, chips are available with four 555 timers in it. These devices are available in circular IC with eight (8), DIP (Dual inline Package) with 8 pins or DIP with 14 pins.
Here is the simple explanation of the 8 pins of 555 Timer.
1. Ground (GND)
It’s the common ground point of the circuit. The ground terminal of external circuit as well as power supply (Vcc) ground terminal is connected with this i.e. GND (Ground) terminal of 555 timer.
2. Trigger
When Trigger terminal gets one –third (1/3) of the supply voltage i.e. Vcc/3 equal amplitude’s negative trigger pulse, then the circuit output changes form Low to High.
3. Output
This terminal is used for getting output and connected with load. At any instant, its value is low or high.
4. Reset
Without taking into account the previous state of output, by providing a trigger pulse to this terminal resets the device. I.e. Its output becomes low.
5. Control Voltage
There are two third positive voltages of the total Supply voltages (Vcc) at control voltage terminal. Thus, it becomes a part of the comparator circuit. Generally, a capacitor is connected between ground and voltage control terminals.
6. Threshold Voltage
Threshold voltage and control voltage is the two inputs of comparator circuit. The circuit compares the available voltage at threshold voltage terminal to the available reference voltage at control terminal.
If the available voltage at threshold terminal (Pin 6) is greater than the control voltage i.e. two-third of Vcc, then the output would be low, otherwise, it would be high.
7. Discharge
When output is low, then Discharge terminal provides a low resistance discharge path to the externally connected capacitor. However, it acts an open circuit, when output is high.
8. +Vcc (Supply Voltage Terminal)
Supply voltage is provided at this terminal for timer operation.
A simple 555 timer circuit is shown below in fig _ which shows the internal construction of 555 timer. According to the fig, the timer contains on two comparators, an RS flip flop, an Output stitch (output buffer) and a Discharge Transistor Q1.
In addition, there are three 5k? resistors are connected in series with 5k? resistor which first end is connected with Vcc (Pin 8 = Supply voltage) and the other end is connected with ground (GND = Pin 1).
Good to Know: due to the three 5k? series connected resistors, this IC timer chip is called 555 Timer J.
Working Principle of 555 Timer
In the 555 Timer block or functional diagram, comparators are those devices which output is high, when their positive input voltage is greater than their negative input voltage and vise versa.
The voltage divider in the circuit (which contains on three series connected 5k? resistors), which provides the trigger level of one-third of Vcc (Vcc/3) and two-third (2/3) of threshold voltage. To understand this point, suppose the input value is 15V. In this case, the value of trigger level would be 5V as (Vcc/3 = 15V/3 = 5V). And the value of threshold level would be 10V as (Vcc x 2/3 = 15V x (2/3)) = 10V.
When needed, the trigger level and threshold can be adjusted by using the Control Voltage terminal (Pin 5) i.e. by changing the control voltage at Pin 5, we may change the trigger level and threshold voltage according to the required specification. However, in this case, the value of trigger and threshold would be remain equal to 1/3 Vcc and 2/3 Vcc respectively.
When the normal high trigger input value instantaneously reduce then the 1/3 Vcc, Then the output of Comparator B becomes High from Low, as a result, RS latch or RS Flip flop goes to “set”. When flip flop goes to set, then Output (at Point 3) becomes high. Simultaneously, the discharge transistor Q1 gets off and The output remains high until the value of normally low threshold input does not increase then the 2/3 Vcc.
As soon as the threshold input increase than the 2/3Vcc, then the output of comparator A becomes Low, as a result, RS flip flop get reset (because the output of comparator is directly connected to the RS flip flop’s input R as shown in the fig). When flip flop gets reset, output becomes low and discharge transistor Q1 goes to on.
The flip flop can be reset by applying external input reset without threshold circuit. Note that, the trigger and threshold inputs (Pin 2 and Pin 6) are controlled by externally components and the 555 timer can be used for Available link for download
Read more »
Wednesday, January 25, 2017
wtat is LCD Display Monitor Problem
wtat is LCD Display Monitor Problem
LCD Display Monitor Problem
Laptop Screen Dim, Blank Or Black

Note that these steps correspond with decision points on the flowchart and are reached through the interactive diamond symbols. The text below cannot be read sequentially.
Do you see a live BIOS splash screen? Most laptops will display a manufacturer splash screen with their brand name, Lenovo, Toshiba, Acer, Sony, etc, before launching into windows. Even those that dont should flash a text screen with the BIOS maker (AMI, Award, Phoenix) in the corner, and a message telling you what key combination to use to access the BIOS Setup screens. A biometric screen prompting you to scan a fingerprint before the system will boot counts as a BIOS splash screen here. If the screen lights up with anything, a graphic or text, it means that the basic display I/O system is functioning.
Return to Diagnostic Chart
Is the screen live if you connect an external display? All notebooks should support an external monitor, usually with a high-density D-Shell 15 pin VGA connector, but some might feature a DVI connector instead. Its a vital part of laptop display troubleshooting to determine if a known good external monitor can be used. Newer laptops dont keep the external connector live by default, and some dont allow for simultaneous display on both the LCD and an external monitor. You can toggle between the notebook screen (which isnt working) and the external display with an Fn key combination. The Fn key is located at the lower left of the keyboard, normally between the CTRL and the ALT key. Toshiba uses Fn-F5 to toggle between the laptop LCD and an external display. IBM or Lenovo uses FN-F7, Acer varies with the model, using Fn-F5, Fn-F3, Fn-F8, Sony Fn-F7, Lenovo Fn-F8, HP or Compaq, Fn-F4. There are variations with the age of the laptop and not all manufacturers have standardized on a key combo across the whole range, but you can usually figure it out from the little graphics on the function keys that line the top of the keyboard.
Return to Diagnostic Chart
Can you hear any sound from the hard drive or fans? If you cant get any life at all on the laptop lcd or the external display, its entirely possible that the problem goes deeper than a video issue. Signs of life include the cooling fan blowing, the hard drive spinning up, any LED activity beyond the LED indicating AC power is attached or battery charging. If the system is powering up, even going through boot as you can often tell by the level of hard drive activity demonstrated by the sound or the hard drive LED flashing, with no life on the LCD or external monitor, you have a board level failure. It could be the video processor failed due to overheating, you can try taking apart and reassembling the laptop body on the chance there is a bus connector failure (its only a possibility on some models), but you dont have to bother inspecting the wiring to to laptop screen or connections in the lid since the external monitor bypasses all of these.
Return to Diagnostic Chart
Do you see a very dim desktop image? Can you see a ghost-like image of your desktop that is functional, ie, one that changes if you drag an icon, launch a program or disappears if you shut down. Standard LCDs produce very little visible light on their own, they require the Cold Cathode Fluorescent Light (CCFL) to light the screen from behind. The fluorescent tube is normally located at the top of the screen, and a bright reflective surface distributes the light across the back of the LCD, so it can shine through the liquid crystals of the liquid crystal display, which only transmit red, green or blue (RGB).
Read More...
Any Kind of Lenovo Problems Call Us
+1-855-517-2433 (Toll Free)
Available link for download
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)